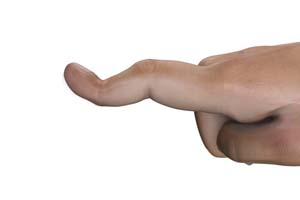
What is Boutonniere Deformity?
Tendons in your fingers connect the muscles in your forearm and hand to the finger bones and help bend and straighten the finger when the muscles contract. Boutonniere deformity is a condition in which a tendon injury to the middle joint of the finger results in the inability to straighten the affected finger.
Causes of Boutonniere Deformity
Boutonniere deformity can occur because of forceful trauma to the top of the middle joint, a laceration to the middle joint or from arthritis.
Symptoms of Boutonniere Deformity
Symptoms associated with this deformity may appear immediately or after a few weeks and may include swelling, pain and restricted movement. In severe cases, a fragment of the bone may be displaced from its original position.
Diagnosis of Boutonniere Deformity
The condition can be diagnosed by a physical examination of the hand, and an X-ray may be ordered to confirm diagnosis.
Treatment for Boutonniere Deformity
Boutonniere deformity can be treated both surgically and non-surgically.
Non-surgical treatments include:
- Application of a splint to the middle joint of the affected finger to straighten it and allow the tendon to heal
- Exercises to improve the flexibility and strength of your fingers
- Protecting your finger by taping it or using protective splints
Surgery is performed when the injury is caused due to rheumatoid arthritis, the tendon is severed, presence of bone displacement or non-surgical treatments fail to provide relief.
Surgical treatments may improve the function of the finger but may not always correct the appearance.
Related Topics
- Wrist Fracture
- Fractures of the Hand and Fingers
- Wrist Sprain
- Flexor Tendon Injuries
- Distal Radioulnar Joint (DRUJ) Arthritis
- Ulnar Nerve Compression in Guyon's Canal
- Scaphoid Facture
- Industrial Hand Trauma
- Distal Radius Osteotomy to Correct Mal-Union (Crooked Painful Wrist)
- Distal Intersection Syndrome
- Distal Biceps Avulsion
- Adult Forearm Fractures
- Arthritis of the Hand and Wrist
- Arthritis of the Thumb
- Ganglion Cyst
- Boutonniere Deformity
- Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
- De Quervain's Tendinosis
- Dupuytren's Contracture
- Hand Pain
- Hand Infections
- Trapeziometacarpal (TMC) Arthritis
- Wrist Injuries
- Wrist Tumors
- Boxer's Fracture
- Swan Neck Deformity
- Carpal Instability
- Bennett's Fracture
- Kienbock's Disease
- Scapholunate Dissociation
- Triscaphoid Joint Arthritis
- Ulnar Carpal Impaction
- Triangular Fibrocartilage Complex Injury (TFCC)
- Guyon's Canal Syndrome
- Hand Masses
- Distal Radioulnar Joint (DRUJ) Instability
- Work Related Hand Injuries
- Wrist Ligament Tear and Instability
- Metacarpophalangeal Joint Arthritis





