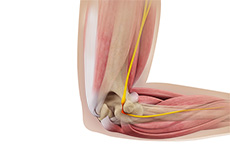
Ulnar nerve neuropathy is the entrapment or compression of the ulnar nerve causing impairment of its function.
Branches from the spinal nerve C8 (cervical) and T1 (upper thoracic) give rise to the ulnar nerve that passes down the arm and into the forearm and hand. The ulnar nerve is one of the three major nerves of the hand that supply the hand muscles and cause their contraction. It provides sensation to the hand, little finger, and half of the ring finger.
Funny Bone: At the inside of the elbow, near the medial epicondyle of the humerus (the bony prominence at the medial side), the ulnar nerve is close to the skin with very little soft tissue to protect or cover it. This region is commonly referred to as the funny bone as hitting this area causes a sudden feeling of shock that often radiates into the hand.
Causes
Factors that cause the entrapment or compression of the ulnar nerve include:
- Thickening of the ligaments at the funny bone region
- Muscle thickness causing nerve compression
- Trauma causing a bone fracture, nerve compression, and/or damage
Symptoms
The symptoms of ulnar nerve neuropathy include:
- Tingling sensation in the ring finger and little finger
- Pain radiating down the forearm into the hand
- Weakening of the hand muscles due to loss of nerve function
- Losing the ability to grip objects and wasting of the muscles (at later stages)
Diagnosis
Your doctor will assess your symptoms and take your medical history. Specific movements may be performed to examine your muscle strength. Gentle tapping at the funny bone region may be performed to observe if you feel abnormal sensations in your ring finger and little finger. Imaging studies (X-ray, MRI, CT-scan) may be ordered. Nerve tests including electromyography and nerve conduction studies may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis.
Treatment
The treatment depends on the severity of the disorder. Your treatment plan may include:
- Bracing of the elbow to prevent excessive flexion
- Rest and activity modification while symptoms subside
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and/or neuromodulatory drugs to manage pain.
- Physical therapy exercises to enhance your flexibility, range of motion and strength.
Surgery may be required if you do not respond to conservative treatment options. Ulnar nerve decompression is performed that involves releasing all compressive tissue around the nerve, most commonly at the elbow. In some cases, the nerve will be transposed or moved to new location to limit tension on the nerve.
Related Topics
- Triceps Injuries
- Osteochondritis Dissecans of the Capitellum
- Elbow Trauma
- Elbow Arthritis
- Bicep Tendon Tear at the Elbow
- Elbow Dislocation
- Triceps Tendonitis
- Elbow (Olecranon) Bursitis
- Elbow Sprain
- Tennis Elbow
- Golfer's Elbow
- Little League Elbow
- Nursemaid's Elbow
- Elbow Pain
- Elbow Contracture
- Distal Humerus Fractures of the Elbow
- Radial Head Fractures of the Elbow
- Elbow Fractures
- Ulnar Nerve Neuropathy
- Loose Bodies in the Elbow
- Radial Tunnel Syndrome
- Lateral Ulnar Collateral Ligament Injuries (Elbow)
- Post-traumatic Stiffness (Elbow)
- Cubital Tunnel Syndrome (Ulnar Nerve Entrapment)





